Design
Overview
The following guide is intended for developers who want to make changes to the Elide framework. It will cover the design of various subsystems.
Module Layout
Elide is a mono-repo consisting of the following published modules:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
| elide-core | Contains modeling annotations, JSON-API parser, and core functions. |
| elide-graphql | Contains the GraphQL parser. |
| elide-async | Contains Elide’s asynchronous and data export APIs. |
| elide-swagger | Contains swagger document generation for JSON-API. |
| elide-standalone | Opinionated embedded Jetty application with JAX-RS endpoints for Elide |
| elide-spring | Parent module for spring boot support |
| elide-spring-boot-autoconfigure | Elide spring boot auto configuration module |
| elide-spring-boot-starter | Elide spring boot starter pom |
| elide-test | JSON-API and GraphQL test DSLs for Rest Assured Testing Framework |
| elide-integration-tests | Integration tests that are run for JPA, Hibernate, and In-Memory data stores. |
| elide-model-config | HJSON Configuration language for the Aggregation store semantic layer. |
| elide-datastore | Parent module for all data stores. |
| elide-datastore-aggregation | Datastore and semantic layer for processing analytic API queries. |
| elide-datastore-hibernate | Parent package for all hibernate and JPA stores. |
| elide-datastore-hibernate3 | Legacy data store for Hibernate 3 support. |
| elide-datastore-hibernate5 | Legacy data store for Hibernate 5 support. |
| elide-datastore-jpa | Primary data store for elide CRUD API queries. Replaces legacy hibernate stores. |
| elide-datastore-mulitplex | Support for multiple data stores. |
| elide-datastore-noop | Zero persistence store. This is used for implementing simple POST functions. |
| elide-datastore-search | Indexed text search store. It must be used in conjunction with the JPA store. |
| elide-datastore-inmemorydb | Hashmap implementation of a datastore. |
High Level Design
The following diagram represents a high level component breakout of Elide. Names in italics represent class names whereas other names represent functional blocks (made up of many classes). Gray arrows represent client request and response flow through the system.
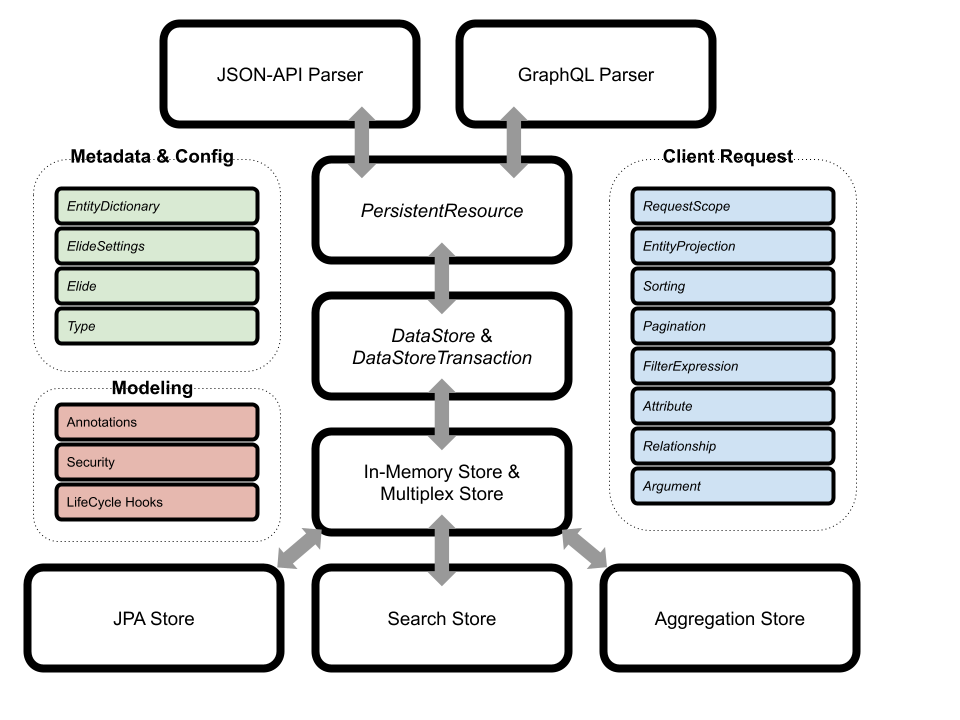
Elide can be broken down into the following layers:
Parsing Layer
The parsing layer consists of a JSON-API parser and GraphQL parser. This layer is responsible for mapping a client request in JSON-API or GraphQL into Elide’s internal request model. The parsers load, create, and manipulate Elide models via the PersistentResource.
Business Logic Layer
The business logic layer is responsible for performing:
- Authorization checks
- Lifecycle hooks
- Audit & Logging
All elide models (once loaded or created) are wrapped in a PersistentResource. All attribute and relationship access (read & write) occur through this abstraction allowing a central place to enforce business rules.
In addition to invoking security checks and lifecycle hooks, the PersistentResource is also responsible for reading and writing the model and its fields to the persistence layer.
Persistence Layer
The persistence layer consists of two abstractions and their concrete implementations:
- A
DataStorewhich is responsible for telling Elide which models it manages and creatingDataStoreTransactionobjects. - A
DataStoreTransactionwhich is created per request and is responsible for saving, loading, and deleting Elide models. Each request’s interactions with the persistence layer should occur atomically.
Elide comes bundled with a number of DataStore implementations. The most notable are the JPA, Search, and Aggregation stores.
Client Request Model
The primary object in the client request model is the EntityProjection. It represents the entire model graph requested by the client. The entity projection consists of Attribute objects (model fields), Relationship objects (named entity projections), and also whether the projection should be filtered, sorted, or paginated. Attribute objects can take Argument objects as parameters.
Metadata and Configuration
Elide is configured either with Spring Boot or the elide-standalone module. Application settings for spring and standalone are mapped to an internal ElideSettings object that configures the Elide framework (denoted by the Elide object).
All static metadata about Elide models is extracted at service boot and stored in the EntityDictionary. This class is used throughout Elide whenever a model must be read from or written to by the PersistentResource.
While earlier versions of Elide represented models as JVM classes, Elide 5 introduces its own Type system. This allows Elide to register and use dynamic models that are not JVM classes.
Modeling
CRUD models in Elide are created from JVM classes whereas analytic models are created either from JVM classes or HJSON configuration files. In either case, Elide annotations are used to add the metadata Elide needs to perform persistence and business rules. All Elide annotations are documented here.
Security Subsystem
Coming Soon.
Analytic Query Subsystem
Coming Soon.