Development
Overview
The following guide is intended to help developers who maintain or want to make changes to the Elide framework.
Building
Elide is built using maven. Because elide is a mono-repo with interdependencies between modules, it is recommended to fully build and install the project at least once:
mvn clean install
Thereafter, individual modules can be built whenever making changes to them. For example, the following command would rebuild only elide-core:
mvn clean install -f elide-core
Pull requests and release builds leverage screwdriver. PR builds simply run the complete build along with code coverage:
mvn -B clean verify coveralls:report.
Release Versions
Elide follows semantic versioning for its releases. Minor and patch versions only have the following version components:
MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH.
Major releases are often pre-released prior to the publication of the final version. Pre-releases have the following format:
MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH-prCANDIDATE. For example, 5.0.0-pr2 is release candidate 2 of the Elide 5.0.0 version.
Release Builds
The release build is triggered by a github tag or release event. Screwdriver will build the project and publish to bintray with the following command:
mvn -B -DskipTests deploy --settings ./settings.xml
To initiate a release, perform the following steps:
- Checkout the Elide source code into a clean directory:
git clone git@github.com:yahoo/elide.git
- Run the following command to build a list of changelog entries since the prior release:
git log $CURRENT_VERSION... --pretty=format:' * [view commit](https://github.com/yahoo/elide/commit/%H) %s ' --reverse- The environment variable
$CURRENT_VERSIONmust be set to the current elide version.
- After the command runs, edit
changelog.mdon the release branch. The file must be hand edited to break the log into sections for Features and Fixes along with a new heading for the current release. Commit the changes and pull them into your local github clone. - Either run:
mvn -B release:prepareif the build is for a patch release.mvn -B release:prepare -DautoVersionSubmodules=true -DreleaseVersion=$NEXT_VERSIONfor all other releases. The environment variable $NEXT_VERSION must be set to the next elide release version.
- Monitor the build and make sure it succeeds in screwdriver.cd.
- In a browser, navigate to https://bintray.com/yahoo/maven/elide
- Navigate to the release tag and then to “Maven Central”
- Navigate to oss.sonatype.org
- Click on profile and then drop down to user token
- Copy the user token key and password into bintray. Click Sync (to publish to maven central). Click Publish (to release on bintray).
Integration Tests
The elide-integration-tests module runs API tests against an embedded Jetty application with an H2 database for persistence. Integration tests are run for the JPA, hibernate, and inmemory stores. The module produce a ‘test-jar’ artifact that is then referenced for each data store module (jpa, hibernate, etc) that runs the corresponding tests.
Not every tests works for every store, and JUnit tags are leveraged to isolate the tests appropriate for each target.
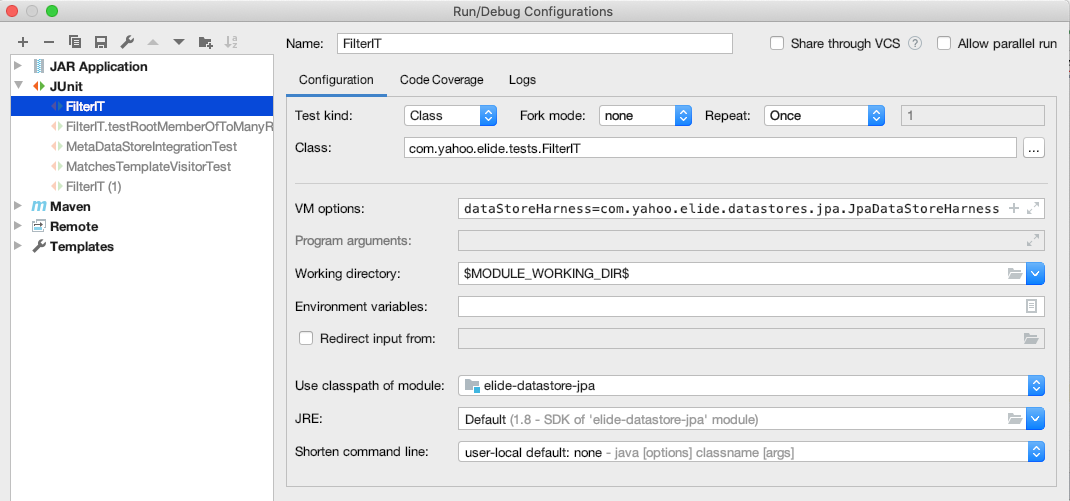
When run in an IDE, the inmemory store is leveraged. To tests against a different data store, the IDE must be configured to:
- Set a property that selects the DataStoreTestHarness which in turn initializes the data store to test.
- Sets the classpath appropriately to the data store submodule that is being tested.
The following screenshot demonstrates configuring these two settings for the ‘FilterIT’ tests in IntelliJ: